
Accrued revenues are recorded as a current asset, while accrued expenses are recorded as a current liability. Businesses should consider the utilization period for their accrued expenses and liabilities when classifying them on the balance sheet. If the https://www.bookstime.com/ service period and payment occur within a span of 12 months, then the accrued liability is classified as short-term.
- Deferred revenue is money received before you provide goods or services.
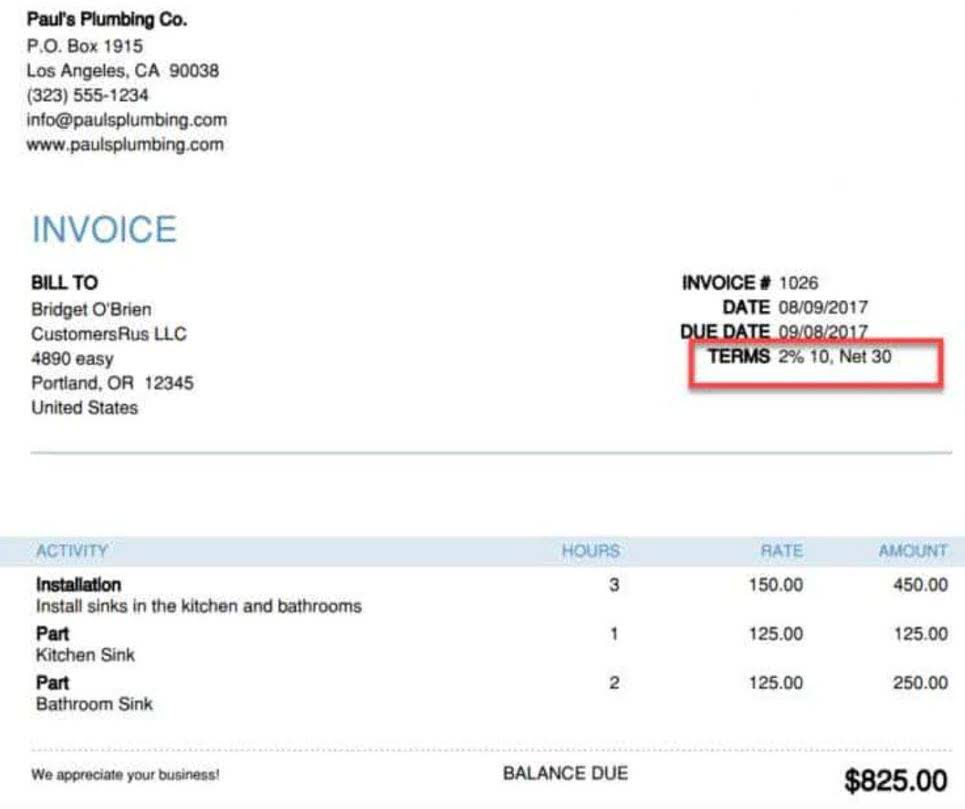
- Suppliers may offer companies discounts for paying on time (or early).
- There are important steps you need to take to record, track, and clear your liabilities.
- Under accrual accounting all expenses are to be recorded in financial statements in the period in which they are incurred, which may differ from the period in which they are paid.
- Just like assets and liabilities, they’re split into two categories, and the current ones are listed by their due date – the most urgent ones first.
- Working capital, calculated as current assets minus current liabilities, is also directly reduced by these accrued items.
Recording and Settling Accrued Expenses
Having a good understanding of the account types is necessary for anyone creating accounts, posting transactions and journal entries, or reading financial reports. Sub-accounts, of course, can be created under any of these five types of accounts. Unlike liabilities, equity is not a fixed amount with a fixed interest rate. The cash receipt is not recognized as revenue until the earnings process is complete. This liability is only reduced, and the corresponding revenue is recognized, when the service is actually rendered to the client. A liability is anything that’s borrowed from, owed to, or obligated to someone else.
- The Matching Principle dictates that expenses must be recognized in the same accounting period as the revenues that those expenses helped to generate.
- On the other hand, expenses are costs incurred to generate revenue and keep operations running.
- This could include loans from a bank, unpaid bills to suppliers, wages owed to employees, or taxes that haven’t been paid yet.
- As such, expenses are a key lever that businesses can use to influence profitability.
- Although both terms relate to a company’s outflow of resources, they represent different financial concepts and have unique impacts on an organization’s financial statements.
Balance Sheet: A No-BS Guide to Accounts, Examples, and the Magic Equation
In this sense, you can consider timing to be an important distinction between liabilities and expenses. This liability will show up on the balance sheet as accounts payable. When the invoice is paid, the liability is removed and the cost is recorded as an expense. Other examples of current liabilities include wages payable, dividends payable, interest payable and unearned revenues—money received in advance for services yet to be completed. Liabilities are listed on your company’s balance sheet and directly impact your business’s assets and equity. There are several types of liabilities, and understanding each one is essential for assessing your business’s financial health and managing future cash flow.
The importance of accrued liabilities
Compliance with tax regulations is also critical when accounting for accrued liabilities. Different jurisdictions may have specific rules on the deductibility of accrued expenses for tax purposes. Companies must stay informed about these regulations to avoid penalties and ensure that their tax filings are accurate and compliant with local laws.
Unlike expenses, liabilities do not directly impact a company’s profitability. Instead, they reflect the company’s financial obligations and its ability to meet those obligations in the future. Liabilities are typically measured in monetary terms and are reported on the balance sheet, providing stakeholders with information about a company’s financial health and solvency. They represent the costs incurred by a business during its normal operations to generate revenue. Expenses can be categorized into various types, such as cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and non-operating expenses. Liabilities, especially long-term ones, affect the company’slong-term financial health.
Current assets
- The loan would be classified as a long-term liability on the balance sheet since it is not due within a year.
- The timing of recognition is another separating factor under the accrual method of accounting.
- The balance sheet isn’t just a static document; it’s a goldmine of data you can use for balance sheet analysis.
- A company may have taken out liability insurance to protect against these financial risks.
- Accrued payroll records wages employees have earned but have not yet collected, plus the employer’s share of taxes and benefits.
- If you are new to HBS Online, you will be required to set up an account before enrolling in the program of your choice.
Understanding the types, importance, and effective management strategies for liabilities is crucial for making informed financial decisions and maintaining a strong balance sheet. Contingent liabilities represent potential financial obligations arising from uncertain future events. Examples include lawsuits, guarantees, or promises that might result in monetary damages if the event occurs. While these liabilities do not have a definite value or outcome, they can significantly impact a company’s financial position are expenses liabilities and creditworthiness. A liability is a financial obligation or debt that requires repayment over time.
Products and services offered through the Rho platform are subject to approval. It records expenses when incurred and creates a matching liability if cash has not yet been paid. Payroll taxes behave like any other current liability, but many business owners overlook them until cash is due. Put differently, an expense measures usage (it reduces net income right away), while a liability measures an obligation (it stays on the balance sheet until you pay).

Balance Sheets 101: What Goes On a Balance Sheet?

Instead of manual entry, our platform allows employees to submit expenses directly through apps like Text Messages, Gmail, Outlook, and Slack, making expense reporting quick and effortless. Contingent liabilities are potential obligations that may arise depending on a future event, such as warranties or pending lawsuits. They are only recorded if the event is likely and the amount is estimable. The Balance Sheet provides a financial status, whereas the Income Statement provides a performance measure. A liability is a balance that carries forward, while an expense is a flow that resets at the end of each reporting period. Liabilities are future-oriented, representing a commitment to a probable future transfer of value.
How to calculate total assets
Due to this, often their equity funds get used to meet expenses, which weakens their financial strength over time. This unpaid obligation is recorded as a liability called Accrued Wages Payable, ensuring the Income Statement reflects the full cost of labor. Similarly, Accrued Interest Payable arises when a firm incurs interest expense balance sheet on a loan, but the cash payment is due later. The interest expense is recognized daily, creating a growing liability until the scheduled payment date.

The current/non-current liabilities are are listed under the liabilities and shareholder’s equity section. As each month passes, a portion of the prepaid asset is consumed, and the Insurance Expense is recognized. This process gradually shifts the value from the Balance Sheet to the Income Statement, ensuring the expense is matched correctly to the period of benefit. Because cash has not yet been paid, a liability (Accrued Expenses or Accounts Payable) is immediately created on the Balance Sheet. The expense is recognized before the cash outflow, establishing the obligation. When the cash is paid later, the liability is reduced, and no new expense is recognized.

Hinterlasse einen Kommentar